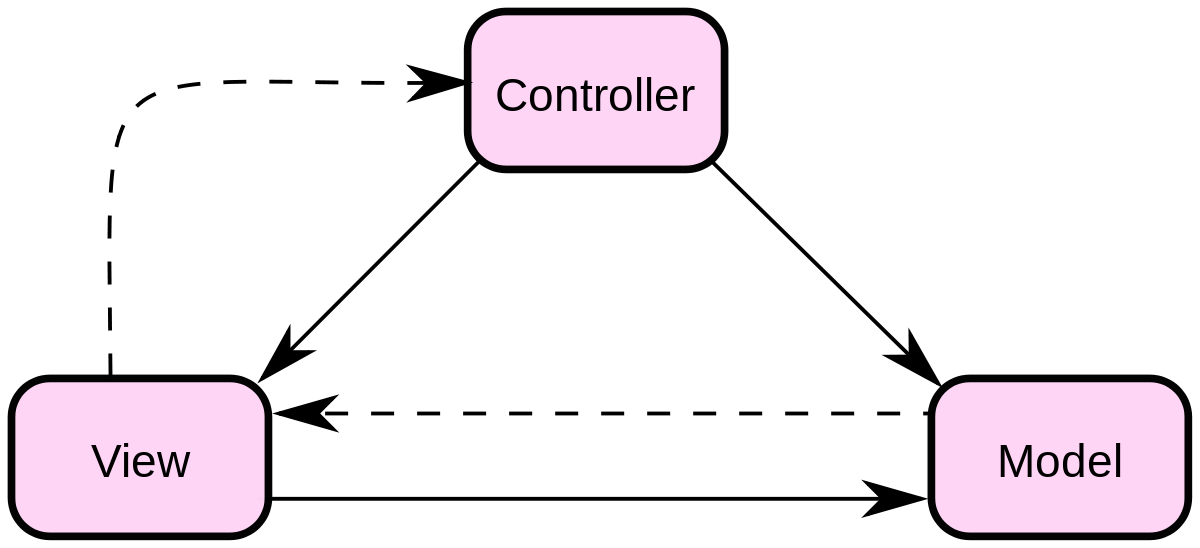
MVC设计模式
- M:Mode,模型:一个功能。用JavaBean实现。
- V:View,视图:用于展示、以及与用户交互。使用html js css jsp jquery等前端技术实现。
- C:Controller,控制器:接受请求,将请求跳转到模型进行处理。模型处理完毕后,再将处理的结果返回给请求处。可以用jsp实现,但是一般建议使用Servlet实现控制器。
Servlet
Java类符合以下规范:
- 必须继承
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet - 重写其中的
doGet()或doPost()方法
doGet():接受并处理所有get提交方式的请求
doPost():接受并处理所有post提交方式的请求
配置
Serlvet2.5需要配置 web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>WelcomeServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.lanqiao.servlet.WelcomeServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>WelcomeServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/WelcomeServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>Servlet执行流程:请求 -> <url-pattern> -> 根据 <servlet-mapping>中的 <servlet-name> 去匹配 <servlet> 中的 <servlet-name> 然后寻找到 <servlet-class> 中将请求交由该 <servlet-class>执行。
手工创建Servlet
- 创建一个类,继承
HttpServlet - 重写
doGet()、doPost()方法 - 配置
web.xml中的Servlet映射关系
Servlet3.0+
要在Servlet类的定义处之上编写注解@WebServlet("url-pattern的值")
匹配流程:请求地址与@WebServlet中的值进行匹配,如果匹配成功,则说明请求的就是该注解所对应的类。
@WebServlet(name = "HelloServlet", urlPatterns = "/HelloServlet")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doPost");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet");
}
}Servlet注解配置细节
| 属性名 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | 指定Servlet 的 name 属性,等价于 <servlet-name>。如果没有显式指定,则该 Servlet 的取值即为类的全限定名。 |
| value | String[] | 该属性等价于 urlPatterns 属性。两个属性不能同时使用。 |
| urlPatterns | String[] | 指定一组 Servlet 的 URL 匹配模式。等价于 <url-pattern>标签。 |
| loadOnStartup | int | 指定 Servlet 的加载顺序,等价于 <load-on-startup>标签。 |
| initParams | WebInitParam[] | 指定一组 Servlet 初始化参数,等价于 <init-param>标签。 |
| asyncSupported | boolean | 声明 Servlet 是否支持异步操作模式,等价于 <async-supported>标签。 |
| description | String | 该 Servlet 的描述信息,等价于 <description>标签。 |
| displayName | String | 该 Servlet 的显示名,通常配合工具使用,等价于 <display-name>标签。 |
注意字符串要有 /,可以只传一个参数,默认为 value
路径
- web.xml中的
/:代表项目根路径(ip:port/projec) - jsp中的
/:服务器根路径(ip:port)
Servlet生命周期
- 5个阶段
- 加载
- 初始化:init(),该方法会在 Servlet被加载并实例化的以后 执行
- 服务:service() 通过doGet(),doPost()
- 销毁:destroy(),Servlet被系统回收时执行
- 卸载
init():
a.默认第一次访问Servlet时会被执行 (只执行这一次)
b.可以修改为Tomcat启动时自动执行
i.Servlet2.5: web.xml
<servlet>
...
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
其中的“1”代表第一个执行。
ii.Servlet3.0
@WebServlet( value="/WelcomeServlet" ,loadOnStartup=1 )
service()调用doGet()/doPost:调用几次,执行几次
destroy():关闭tomcat服务时,执行一次。HttpServletRequest中的方法:(同request),例如setAttrite()、getCookies()、getMethod()
HttpServletResponse中的方法:(同response)
获取常见内置对象
- out:
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); - session:
request.getSession(); - application:
request.getServletContext();
三层架构
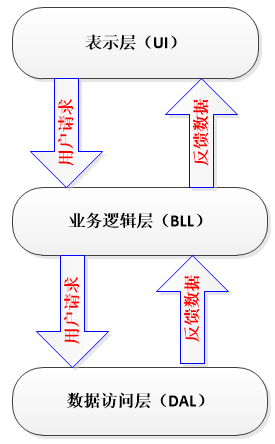
- UI(表现层): 主要是指与用户交互的界面。用于接收用户输入的数据和显示处理后用户需要的数据。位于
xxx.servlet包中。 - BLL:(业务逻辑层): UI层和DAL层之间的桥梁。实现业务逻辑。业务逻辑具体包含:验证、计算、业务规则等等。位于
xxx.servic/manager/bll包中 - DAL:(数据访问层): 与数据库打交道。主要实现对数据的增、删、改、查。将存储在数据库中的数据提交给业务层,同时将业务层处理的数据保存到数据库。(当然这些操作都是基于UI层的。用户的需求反映给界面(UI),UI反映给BLL,BLL反映给DAL,DAL进行数据的操作,操作后再一一返回,直到将用户所需数据反馈给用户)位于
xxx.dao包中
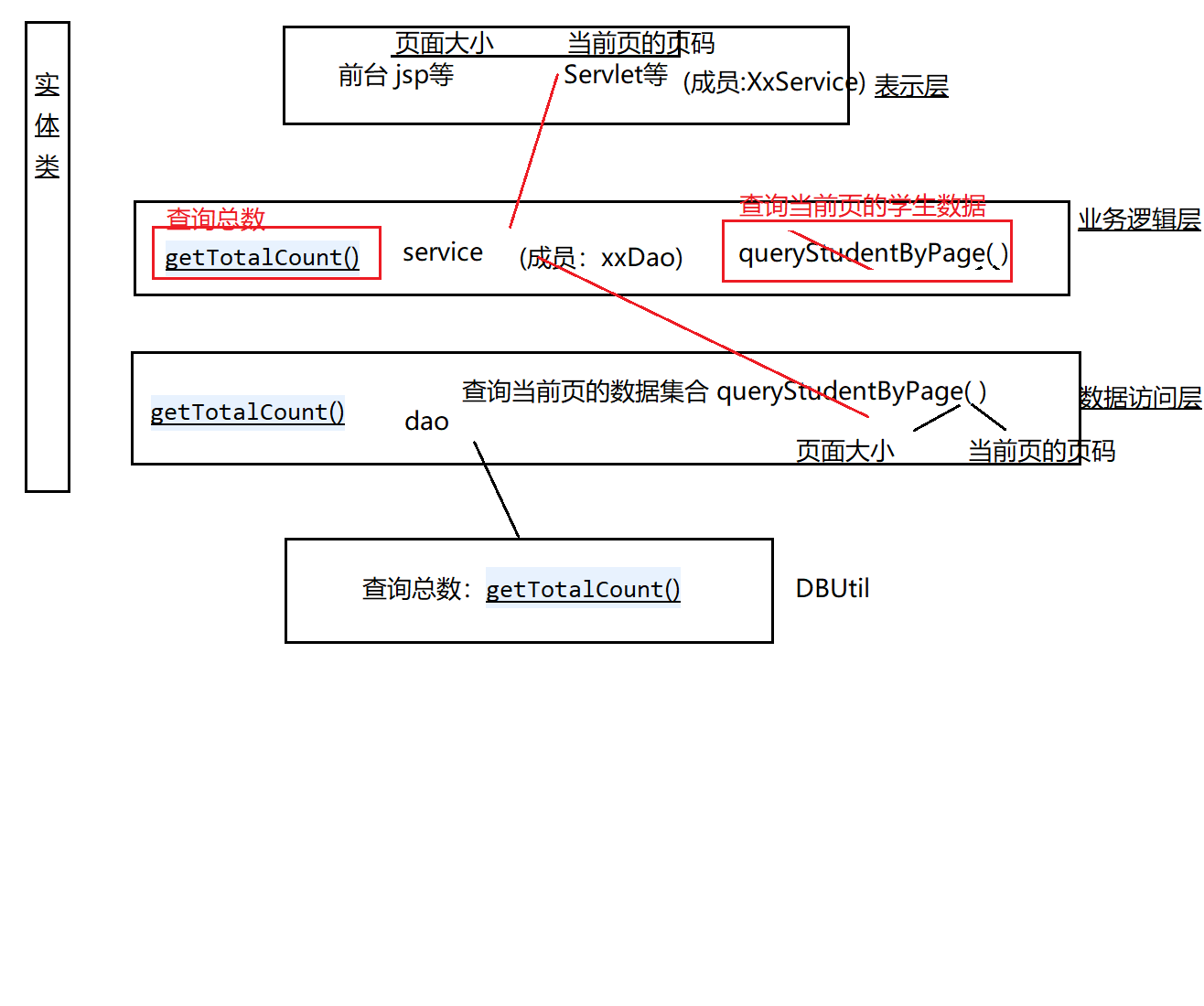
三层架构与MVC
表示层:V前端,C后台
业务逻辑层,数据访问层(原子性),实体类:M
三层优化
加入接口
- 面向接口开发:先创建接口-再实现类
- service、dao加入接口
接口与实现类的命名规范
接口:interface, 起名 I实体类Service IStudentService IStudentDao 实现类:implements 起名 实体类ServiceImpl StudentServiceImpl StudentDaoImpl 接口:I实体类层所在包名 IStudentService、IStudentDao 接口所在的包:xxx.service xx.dao 实现类:实体类层所在包名Impl StudentServiceImpl、StudentDaoImpl 实现类所在的包:xxx.service.impl xxx.dao.impl以后使用接口/实现类时,推荐写法:
接口 x = new 实现类(); IStudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl();
DBUtil 通用的数据库帮助类,可以简化Dao层的代码量
- 帮助类 一般建议写在 xxx.util包
- dao和DBUtil的区别:dao是处理特定类的数据库操作类,DBUtil是通用数据库操作类
参考链接:
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35038153/article/details/77484185
- https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/three-tier-architecture.html
版权属于:moluuser
本文链接:https://archive.moluuser.com/archives/36/
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。


